Abscess: A circumscribed collection of purulent exudate appearing in an acute or chronic, localized infection, caused by tissue destruction and frequently associated with swelling and other signs of inflammation and pain.
Abducens nerve: Cranial nerve # 6. Innervates the lateral rectus, which abducts the eye (moves the eye out); located in the superior orbital fissure.
Accessory nerve: Cranial nerve # 11. Controls the muscles of the neck and overlaps with functions of the vagus nerve; located in the jugular foramen.
Acrochordons: A polypoidal outgrowth of both epidermis and dermal fibrovascular tissue; also known as a skin tag.
Acropachy: subperiosteal new bone formation.
Actinic keratosis: A pre-malignant warty lesion occurring on the sun exposed skin of the face or hands in older fair skinned people.
Adenocarcinoma: A malignant neoplasm of epithelial cells in a glandular or gland-like pattern.
Adenoid cystic carcinoma: A histologically defined type of carcinoma characterized by round, gland-like spaces or cysts bordered by layers of epithelial cells without intervening stroma.
Adenoma: An ordinarily benign neoplasm of epithelial tissue in which the tumor cells form glands or gland-like structures in the stroma; usually well circumscribed, tending to compress rather than infiltrate or invade adjacent tissue.
Adipose tissue: Fatty tissue.
Adnexa: Appendages of the eyeball, including the soft tissue, muscles and eyelids.
Afferent pupillary defect: A condition of the eye where the pupil does not constrict appropriately to the level of light reaching it. It is very important in the evaluation of optic nerve function.
Albright syndrome: Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia with irregular brown patches of cutaneous (skin) pigmentation and endocrine dysfunction, especially precocious puberty in girls.
Angiotensin converting enzyme: An enzyme that catalyses the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor.
Ankyloblepharon: Fusion of the eyelids to each other along the lid margins.
Annulus of Zinn: A ring of fibrous tissue surrounding the optic nerve at its entrance at the apex of the orbit. It is the origin for five of the six extraocular muscles.
Anophthalmic socket: An eye socket that lacks an eyeball.
Anophthalmos: Congenital absence of all tissues of the eyes.
Apert syndrome: Disorder characterized by craniosynostosis and syndactyly; associated with hearing loss; mental retardation is a variable feature.
Arcus marginalis: Collection of fibrous tissue where the orbital septum meets the orbital rim.
Arteriovenous fistulas: An abnormal communication between an artery and vein, usually resulting in the formation of an arteriovenous aneurysm.
Arthritis giant cell: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a type of vasculitis or arteritis, a group of diseases whose typical feature is inflammation of blood vessels.
Aspergillosis: A type of fungal infection. Usually affects immune compromised hosts.
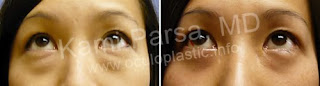
Asian Blepharoplasty: Cosmetic eyelid surgery for Asians. This procedure is usually done to decrease upper eyelid fullness and reduce the epicanthal fold that is common in Asians.